Posts Tagged ‘mvc’
Caching in MVC 5 Asp.net
Hello Everyone,
In this blog I want to share advantages of caching in MVC. Its a very important to know how caching is used in MVC websites.
By using Caching, we can store content at client’s browser and/or server. We can easily access these data and content when required.Caching data or content provides following advantages:
- Minimize Request To Hosting Server
- Minimize Request To Database Server
- Reduce Network Traffic
- Save Time and resources
- Above advantages helps in improving the performance of MVC Website.
There are two types of method for caching available in MVC.
- Page Output Caching
- Application Caching
In this blog we will discuss on Page Output Caching.We can achieve this by
adding OutputCache attribute to either an individual controller action or an
entire controller class.
OutputCache Filter Parameter :
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CacheProfile | string | It is the name of the output cache profile which is defined with in tag of Web.config. |
Example: Creating Cache profile in cache.
<caching>
<outputCacheSettings>
<outputCacheProfiles>
<add name=”Test1″ duration=”30″ varyByParam=”none”/>
</outputCacheProfiles>
</outputCacheSettings>
</caching>
And this cache profile is used in the action method as shown below.
[OutputCache(CacheProfile = “Test1”)]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | int | It specify the duration in sec to cache the content. |
Example : The output of the Index() action is cached for 30 seconds.
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[OutputCache(Duration=30, VaryByParam=”none”)]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
Note: If you will not defined the duration, it will cached it for
by default cache duration 60 sec.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Location | OutputCacheLocation | It specify the location of the output to be cached. Location property can be any one of the following values:
|
Example: Cache stored at client browser.
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.UI;
namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers
{
public class UserController : Controller
{
[OutputCache(Duration=3600, VaryByParam=”none”, Location=OutputCacheLocation.Client)]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VaryByParam | string | This property enables us to create different cached versions of the very same content when a form parameter or query string parameter varies. If not specified, the default value is none. VaryByParam=”none” specifies that caching doesn’t depend on anything. |
| VaryByCustom | string | This is used for custom output cache requirements |
| VaryByHeader | string | This specify list of HTTP header names that are used tovary the cache content. |
Example:
public class TestController : Controller
{
[OutputCache(Duration = 30, VaryByParam = “none”)]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[OutputCache(Duration = 30, VaryByParam = “id”)]
public ActionResult Index1()
{
return View();
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NoStore | bool | It enable/disable where to use HTTP Cache-Control. This is used only to protect very sensitive data. |
| SqlDependency | string | It specify the database and table name pairs on which the cache content depends on. The cached data will expire automatically when the data changes in the database. |
For more information visit here
I hope this will help you.Your valuable feedback and comments are important for me.
ASP .NET MVC Life Cycle
Hello Everyone,
In this blog we will discuss life cycle for ASP.NET MVC. Before starting with MVC, it’s a very important to know that how does your request process.
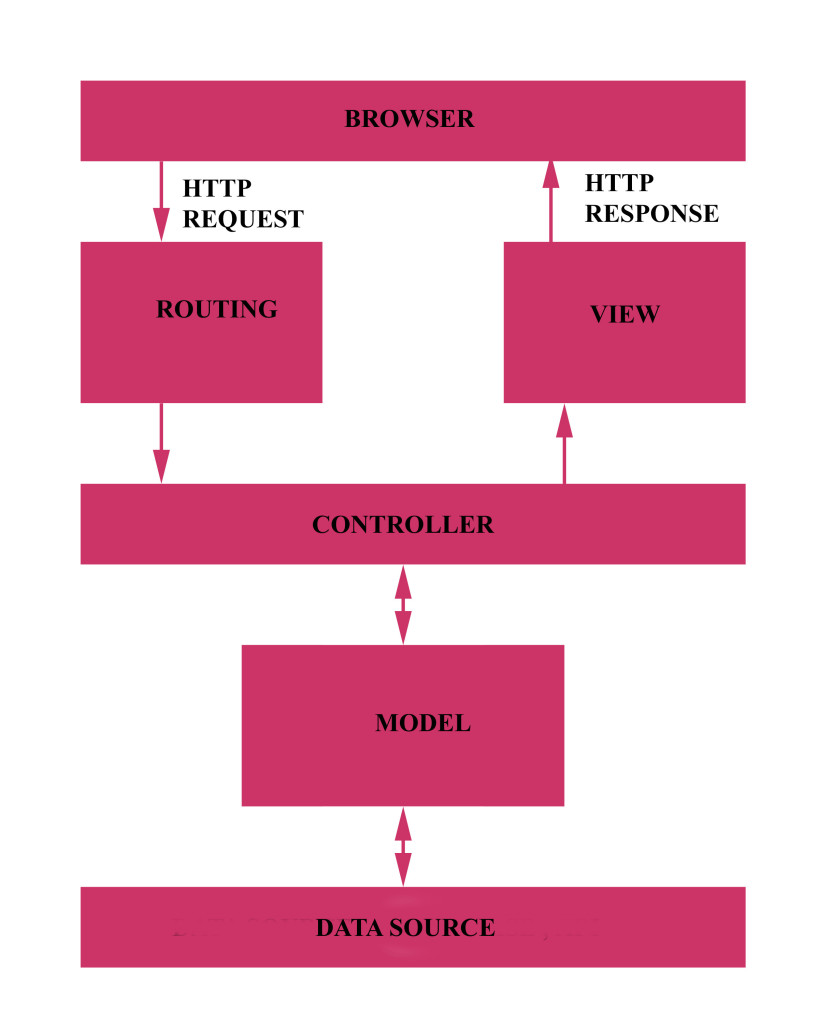
In above figure I tried to show how MVC application process. Your browser sends and receive request in form of HTTP Request and HTTP Response respectively. Routing is a process in which it analyzes the request and invokes an Action of the appropriate Controller. Action calls appropriate method of the model.The Model communicates with the data source (e.g. database or API). Once the Model completes its operation it returns data to the Controller which then loads the appropriate View. The View executes presentation logic using the supplied data. In the end, an HTTP response is returned to the browser.This is just a quick view of MVC life-cycle.
Let’s see details view of MVC life cycle.
This is performed by following steps.
- Receive first request for the application: An MVC application contains only one Route Table. The Route Table maps particular URLs to particular controllers. Check below code of Global.asax: Routes objects are add to RouteTable object when application starts first.The Application_Start() method is invokes only once when the very first page is requested.
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
public static void RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilterCollection filters)
{
filters.Add(new HandleErrorAttribute());
}
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute(“{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}”);
routes.MapRoute(
“Default”, // Route name
“{controller}/{action}/{id}”, // URL with parameters
new { controller = “Home”, action = “Index”, id = UrlParameter.Optional } // Parameter defaults
);
}
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
}
}
- Perform routing : When we make a request in MVC, UrlRoutingModule reads these request to create a RequestContext object.When requested URL found in RouteTable, the Routing engine forwards the request to the corresponding IRouteHandler for that request. The default one calls the MvcHandler. The routing engine returns a 404 HTTP status code against that request if the URL patterns is not found in the Route Table.
- Create MVC request handler: MVC handler implements IHttpHandler interface and further process the request by using ProcessRequest method.When ProcessRequest() is called on the MvcHandler object created, a new controller is created, as show in below code.
- Create and Execute controller: The controller is created from a ControllerFactory. This is an extensibility point since you can create your own ControllerFactory. The default ControllerFactory is named, appropriately enough, DefaultControllerFactory.The RequestContext and the name of the controller are passed to the ControllerFactory. CreateController() method to get a particular controller. Next, a ControllerContext object is constructed from the RequestContext and the controller. Finally, the Execute() method is called on the controller class. The ControllerContext is passed to the Execute() method when the Execute() method is called. For reference check below code.
virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
SecurityUtil.ProcessInApplicationTrust(delegate {
IController controller;
IControllerFactory factory;
this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out factory);
try
{
controller.Execute(this.RequestContext);
}
finally
{
factory.ReleaseController(controller);
}
});
}
- Invoke action:The Execute() method finds a action of the controller to execute. Controller class can be created by us and Execute() method finds one of the methods that we write into the controller class and executes it.
- Execute result: Action method of controller receives the user input data, process these data and returns result. The built-in result types can be ViewResult, RedirectToRouteResult, RedirectResult, ContentResult, JsonResult, FileResult, and EmptyResult.
For more details Visit HERE
I hope this will help you.Your valuable feedback and comments are important for me.